At the Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence, we are at the forefront of pioneering research that pushes the boundaries of AI and its real-world applications...
This section highlights some of our latest AI-driven innovations, showcasing groundbreaking research, novel methodologies, and impactful applications that are shaping the future.
Research Area: Multimodal AI, Transformers

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
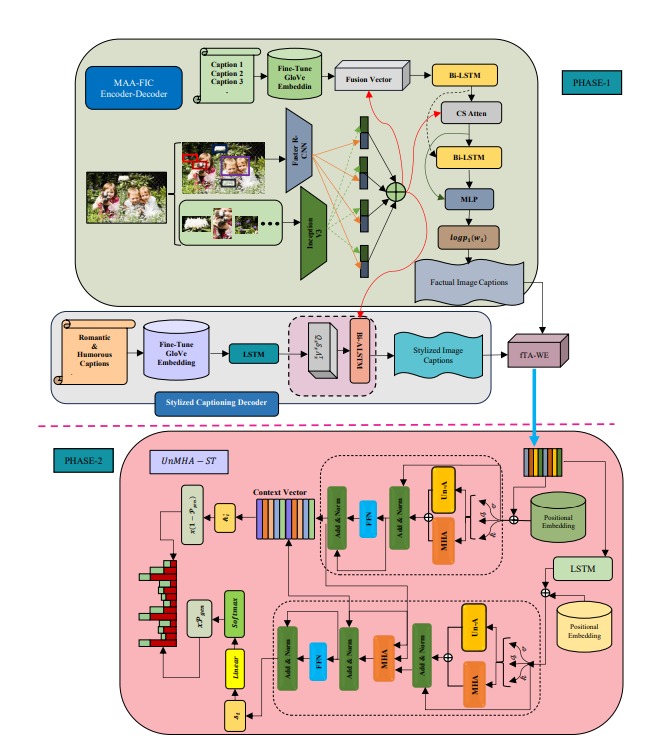
Sharma, D., Dhiman, C., & Kumar, D. (2025). UnMA-CapSumT: Unified and Multi-Head attention-driven caption summarization transformer. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 104600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2025.104600, 2025
Research Area: Computer Vision, Deep Learning & Attention mechanisms

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity School of Engineering and Technology
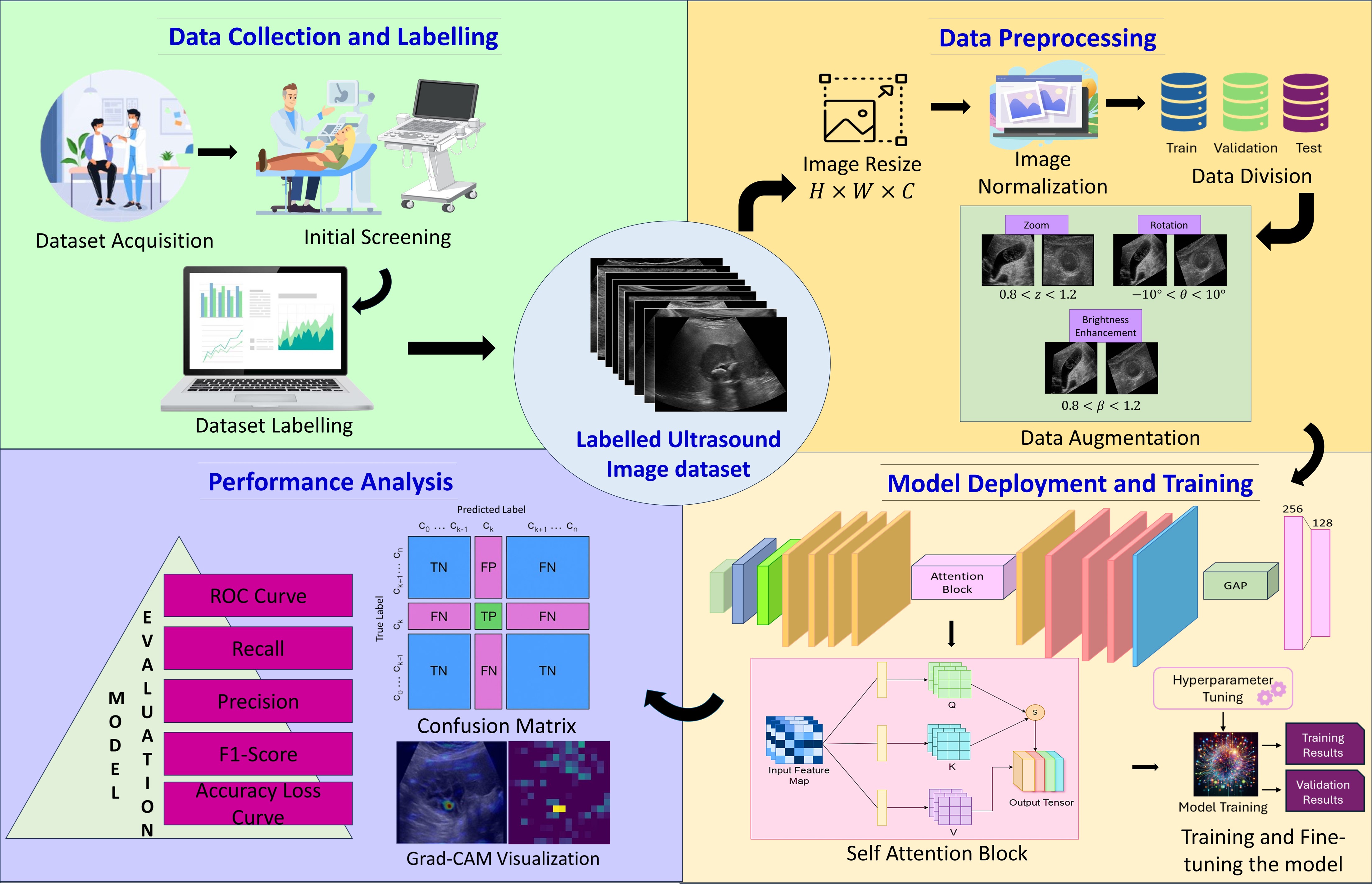
Research Area: Chronic Pain Classification, Large Language Models (LLMs), Deep Learning, Diagnostic Decision Support Systems (DDSS), Multimodal AI, Clinical Text and Imaging Analysis, Electronic Health Records (EHR)

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
Key Benefits:
The Project is Funded by ICMR. Joint collaboration between Amity University (Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence), the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), and Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS), Lucknow.
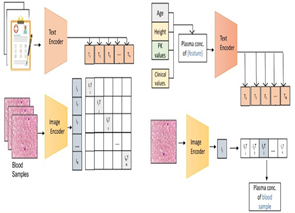
Research Area: Deep Learning, Artificial Intelligence in Pharmacokinetics and Tuberculosis Treatment, Precision Medicine and Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, Multi-modal model

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
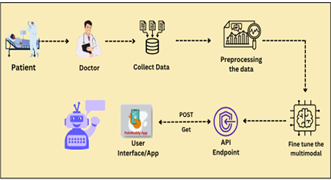
The Project is Funded by ICMR. Joint effort between Amity University (Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence) and ICMR-NIRBI (Indian Council for Medical Research- National Institute for Research in Bacterial Infections).
Research Area: Large Language Moldes (LLMs), Deep Learning, Diagnostic Decision Support Systems (DDSS), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Electronic Health Records (EHR)

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
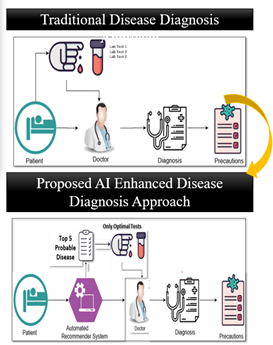
Key Benefits:
The Project is Funded by ICMR. Joint effort between Amity University (Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence) and ICMR-NIE (Indian Council of Medical Research - National Institute of Epidemiology).
Research Area: Deep Learning and Brain-computer interfaces

B.Tech CSE Student (2020-24) Amity School of Engineering & Technology

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
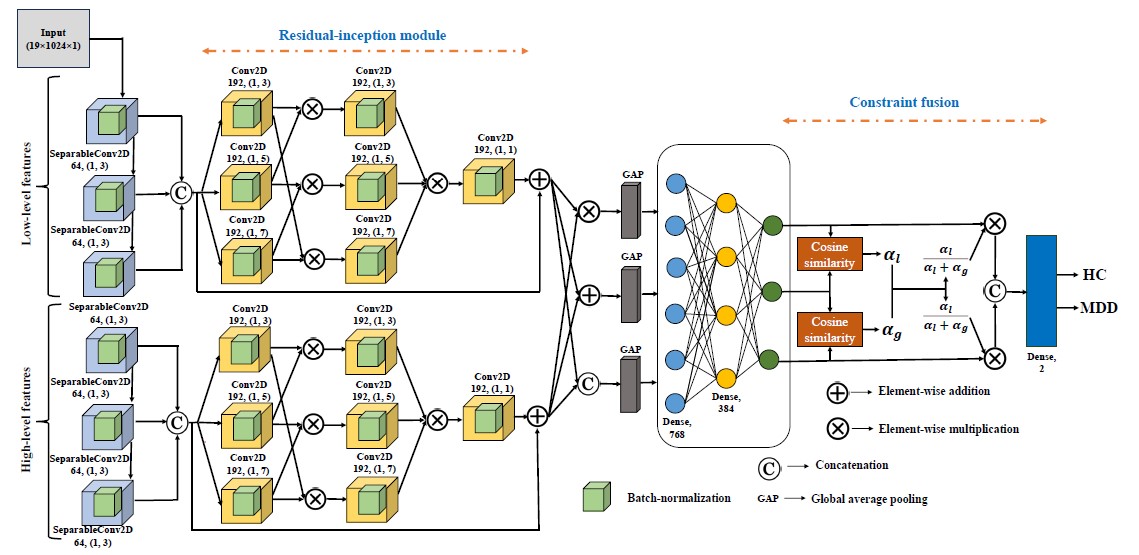
Research Area: Deep learning, Computer Vision.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
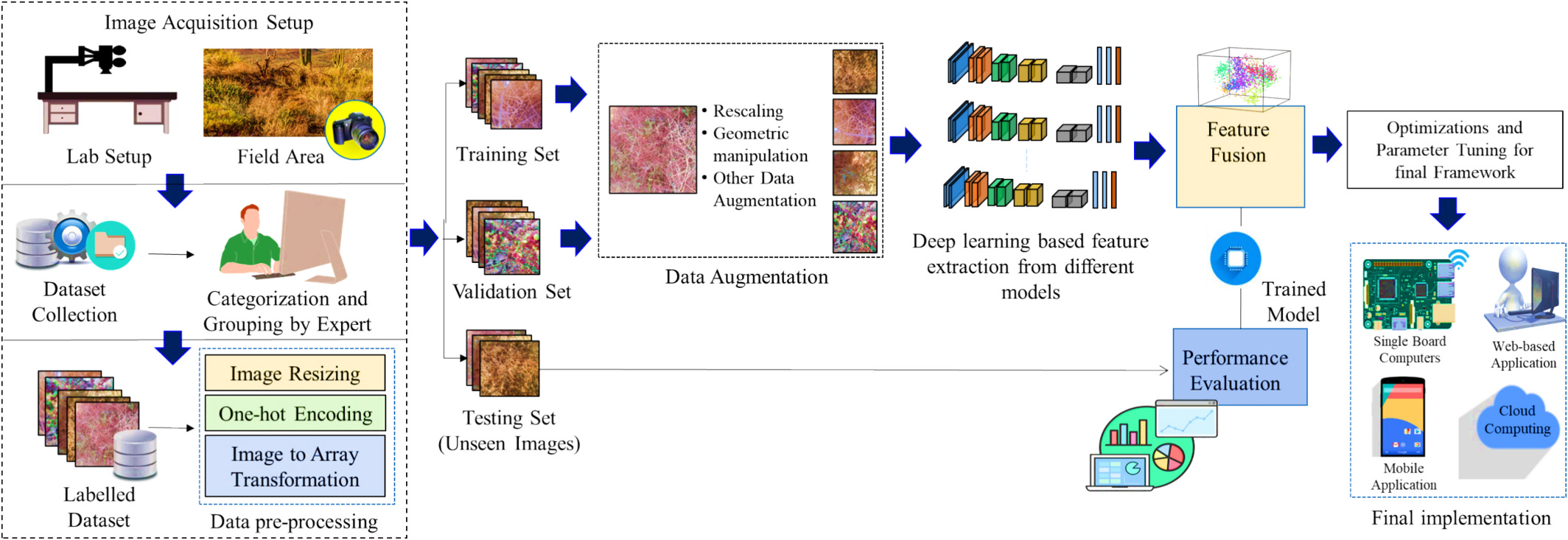
Key Highlights
AgriDeep-Net, a multi-model deep learning framework, enhances fine-grained agricultural image classification by fusing features from diverse architectures. It effectively tackles low inter-class discrimination, uneven data distribution, and intra-class diversity for precise multi-class crop analysis.
Rakesh Chandra Joshi, Radim Burget, Malay Kishore Dutta, 2025. “AgriDeep-net: An advanced deep feature fusion-based technique for enhanced fine-grain image analytics in precision agriculture”. Ecological Informatics. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2025.103069, 2025, SCI Indexed Impact Factor: 5.9.
Research Area: Machine Learning and Robotics

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
.png)
Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.

Research Area: Deep Learning, Computer Vision.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
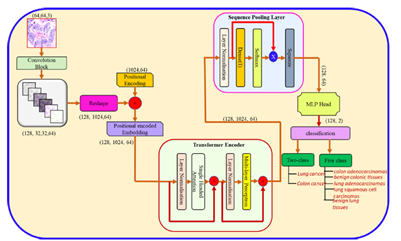
Research Area: Machine Learning/Computer-aided Diagnosis

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
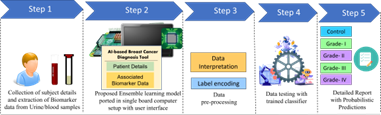
Research Area: Computer Vision, Deep Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
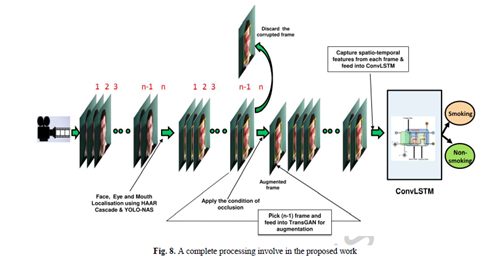
Research Area: Deep Learning / Assistive Device

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.

Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
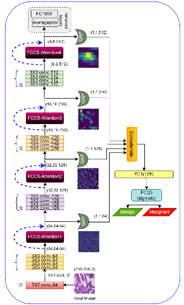
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
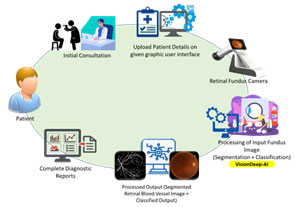
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning
.png)
Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
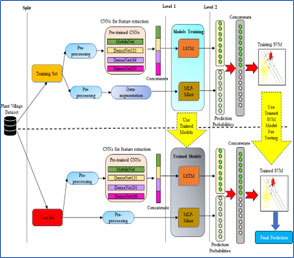
Research Area: Time series analysis / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
.png)
Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
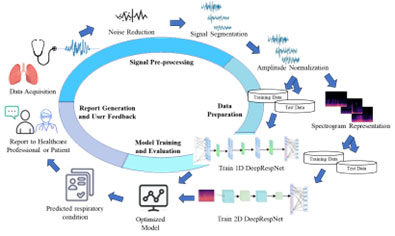
Research Area: Time series analysis / Deep Learning /Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
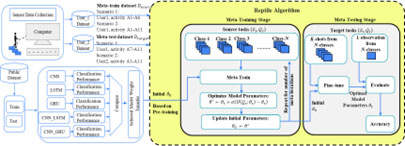
Research Area: Deep learning/ Human machine interaction

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
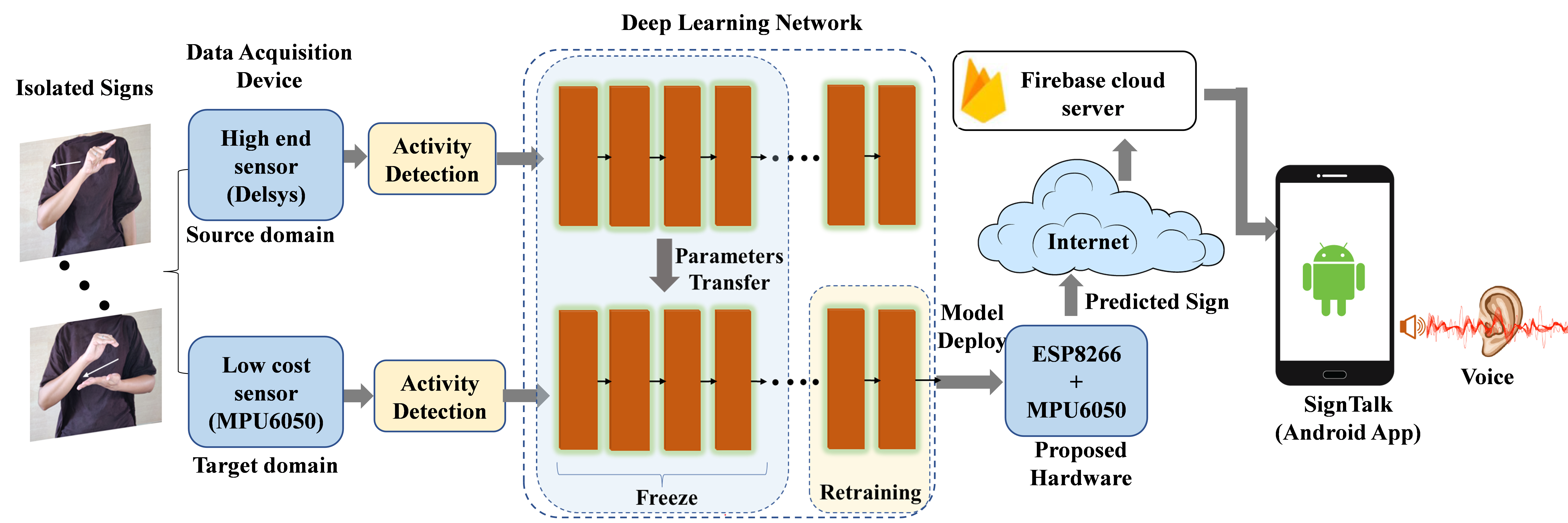
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
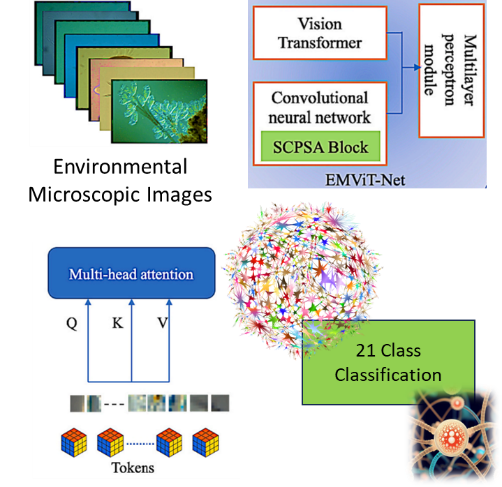
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning

AI Scientist Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
Research Area: Time series analysis / Deep Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
Research Area: Artificial Intelligence/Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
Research Area: Brain-computer Interface / Deep Learning.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence.
Geet Sahu et al. "Single Image Dehazing via Fusion of Multi-level Attention Network for Vision-Based Measurement Applications." IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3271753, 2023, Impact Factor – 5.6.
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Institute of Environmental Toxicology, Safety and Management
Research Area: Time series analysis / Deep Learning

AI Scientist Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

AI Scientist Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence
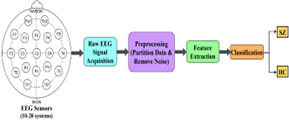
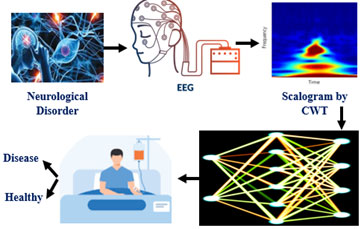
Geet Sahu, K.Mohan et.al. “A Pyramidal Spatial-based Feature Attention Network for Schizophrenia Detection using Electroencephalography Signals” IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2023.3314639, 2023, Impact Factor – 5.
Research Area: Deep Learning / Time Series Analysis/ Transfer Learning

Amity School of Engineering and Technology Amity University Uttar Pradesh

Amity School of Engineering and Technology Amity University Uttar Pradesh
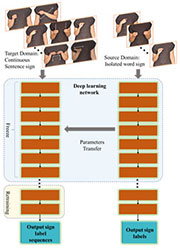
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity School of Engineering and Technology

Amity School of Engineering and Technology
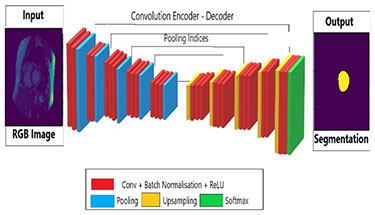
Research Area: Computer Vision / Deep Learning / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Institute of BioTechnology

Amity Institute of BioTechnology
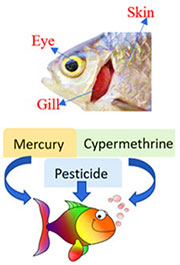
Research Area: Deep Learning / Computer Vision / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Institute of Virology & Immunology

Amity Institute of Virology & Immunology
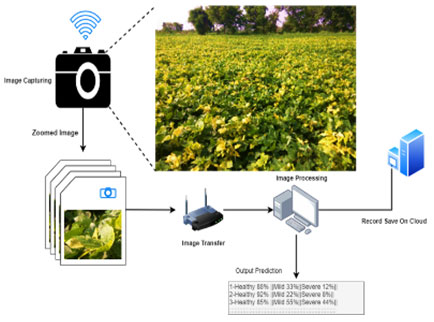
Research Area: Deep Learning / Computer Vision / Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Institute of BioTechnology

Research Area: Computer Vision/ Machine Learning

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity Food and Agriculture Foundation
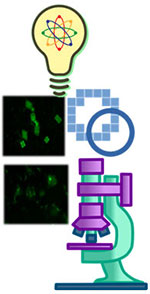
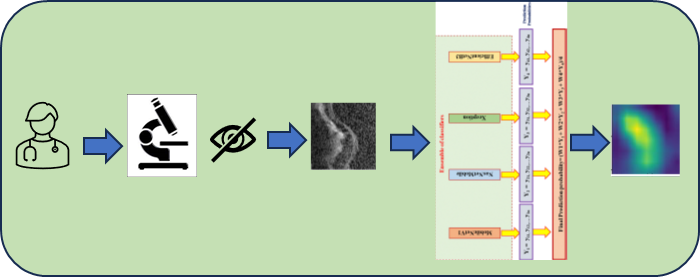
Rakesh Chandra Joshi, Saumya Dhup, Nutan Kaushik, Malay Kishore Dutta, "An efficient oil content estimation technique using microscopic microalgae images", Ecological Informatics, doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2021.101468, 2021, Elsevier Publishers, SCI indexed Impact Factor – 4.498.
Research Area: Deep Learning / Artificial Intelligence / Computer Vision

Amity Centre for Artificial Intelligence

Amity School of Engineering and Technology
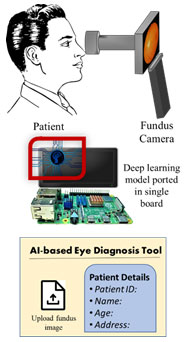
Research Area: Deep Learning / Capsule Networks/ AI-based device

Amity School of Engineering and TechnologyAmity University Uttar Pradesh

Student B.Tech, ECEAmity School of Engineering and TechnologyAmity University Uttar Pradesh
