Amity Center of Pollution Control
Introduction
Amity University Haryana developed a robust infrastructure for Air Quality monitoring in collaboration with leading national (IITM) and international (NASA) research organizations. Amity Center of Ocean And Atmospheric Research (ACOAST) is nodal center carrying out climate related activities including awareness programme, episodic survey, campus based projects and capacity building sessions in coordination with government agencies. Online display of campus Air Quality parameters (including PM10. PM2.5, Ozone, NOX, SOX etc) act pivotal role in creating mass awareness among students, faculty and nearby community as Delhi NCR turned into a gas chamber during winters. The Climate research and action infrastructure related with monitoring and data sharing includes.
Air Quality Monitoring Station (AQMS)
An Air Quality Monitoring Station (AQMS) at Amity University Haryana Campus is result of academic collaboration of Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune with objective of data sharing, research and creating mass awareness for climate and pollution issues. The online monitoring of 22 critical air quality parameters, including particulate matter, Green House Gases including carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx, NO2, NO),and other gases is displayed on a large screen to provide a comprehensive view of air quality in and around the AUH campus. This monitoring station plays a key role in contributing to a national.

Fig: Front-view with data display Fig: Rack-mounted inside the AQMS
network of air quality stations, whose data collectively forms a vital emission inventory. This inventory helps in creating predictive models that forecast local and regional air quality, guiding policy decisions and public health advisories. The detailed data collected here is crucial in identifying pollution sources, understanding trends, and supporting initiatives aimed at reducing air pollution.
This visible information empowers students, staff, and visitors to make informed decisions about their daily activities, such as avoiding outdoor exercise during high pollution periods. The station thus serves not only as a scientific tool but also as an educational resource, enhancing awareness of air pollution and its potential health impacts among the campus community and the general public.
NASA-AERONET Global Network Station
In a significant collaborative research effort, a NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration, USA) AERONET (AErosol RObotic NETwork) global network station has been continuously operating at university campus. It is designed for continuous, real-time monitoring of aerosols under clear-sky conditions, contributing to Regional and Global Air Quality, Water, Energy, and Climate Research. The data collected from this station supports critical environmental research and enhances understanding of atmospheric processes at both local and global scales.
The data portal provides column-integrated aerosol optical depth (AOD), aerosol size distribution, refractive index, fine-mode and coarse-mode aerosol fractions and single scattering albedo (SSA). This data set is critical to understand extent of global warming at local and regional scale. The data generated from this AERONET station is not only used for scientific research but also feeds into global models that inform policy decisions, improve air quality forecasts, and support initiatives to mitigate climate change. Furthermore, the station serves as a valuable educational tool for students and researchers at AUH, offering real-time data that enriches their understanding of atmospheric science and the critical role aerosols play in the Earth’s energy balance and ecosystem health.
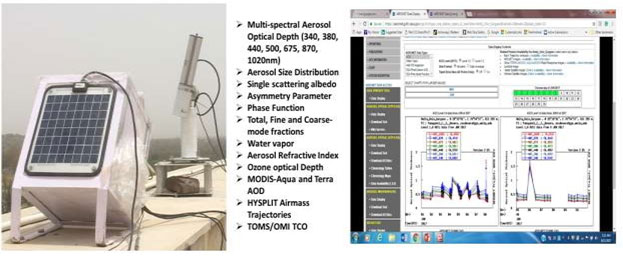
Fig. NASA’s AERONET Fig. AERONET Data Portal
© 2021 Amity University Gurugram. All Rights Reserved.
