Herein, we report the synthesis of Novel nanocomposites (NCs) prepared by azide-functionalized polystyrene coupled with alkyne-functionalized nanographite platelets (NGPs) by using copper(I) catalyzed azide–alkyne click chemistry. The electrical properties of the click nanocomposites were found to posses the resistance of NGPs loading. The C-NCs with fast response, rapid recovery and excellent repeatability at room temperature provide novel materials for chemiresistive sensors for detection of H2O2 vapors. DOI: 10.1039/c5ra10952c.
Utilization of Click Chemistry for Therapeutic Implications of Superoxide Dismutase in Kinase Drug DiscoveryIn recent years, several scientific investigations have reported the therapeutic implications of superoxide dismutase (SOD) against oxidative stress and -induced pathology in clinical and preclinical trials. Indeed, various kinase, molecular signaling and physiological process has altered by reactive oxygen species. Click chemistry including bioconjugation and cyclo-addition are the most prominent methods to produce highly efficient SOD formulations. DOI: 10.2174/1568026617666170307112837
Stimuli Responsive Polymers via Click ChemistryWe are also involved in environmentally effective polymers which change their phase with the effect of temperature, pH, Light, magnetic, etc (doi.org/10.1039/C3PY01648J). We can design polymers according to the requirements and appropriate stimuli. We also checked the solution concentration effect on the synthesis of clickable polymers to obtain intermolecular or/and intramolecular polymers. (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134%2FS1560090419060095)
Triazole-Containing Hydrogels for Time-Dependent Sustained Drug ReleaseThe purpose of this study is to develop novel triazole‐containing hydrogels (TGs) as drug carrier and to investigate the sustained drug release accomplished by their time‐dependent swelling behavior. The synthetic pathway of TGs includes: (1) DCC‐coupling on hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) to prepare HEMA‐alkyne (HA), (2) click‐coupling to prepare a triazole‐ring‐containing monomer (TM), and (3) the synthesis of a series of TGs. The aggregation between triazole rings is found to be responsible for drug release controllability. Rhodamine 6G is studied as a model anticancer drug for release experiments. The effects of pH and temperature on the properties of sustained drug release are also studied. DOI: 10.1002/marc.201300585
For the first time we reported electrochemical preparation of exceptionally biocompatible, highly crystalline, and well exfoliated nitrogen doped graphene nanosheets (eNGS) from carbon nanosheets for the development of mighty platforms in the field of modern biosensing and other biological applications for human welfare. (DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00616-8 )
The rising incidence of antibiotic resistance has led to an increasing need for developing novel and efficient antimicrobial products that can counter infections. The antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of N-doped carbon nanosheets (CNS) was examined for gram negative E. coli. (DOI : 10.1039/c4ra17049k) We envisioned that the physical stress and piercing action caused by sharp “knife- edges” as well as the presence of heteroatoms in CNS result in the rupturing of the bacterial cell wall, eventually causing cell death.
We are working towards developing a variety of physically cross linked, pH sensitive SMART hydrogels and their nano-composites with tunable formulations, possessing microporous interiors , resembling a honeycomb framework, with a continuous skin on the surface using different variety of monomers. Our formulations, being devoid of any chemical cross linkers found to be highly biocompatible which opens a gateway for myriad of biomedical applications.
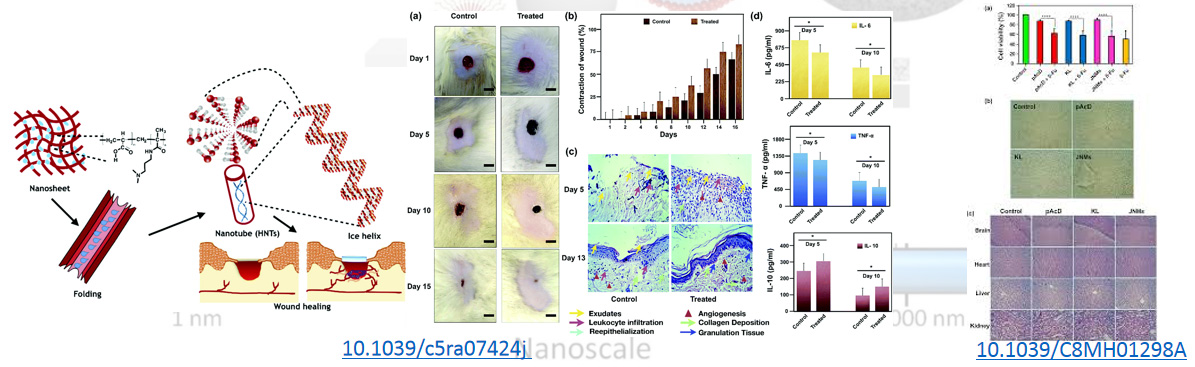
Drug deliveryThere is often a design trade-off between effective drug delivery and favorable physicochemical properties however we have engaged in research that address bottlenecks in designing several unique framework of hydrogels which have good controllability for releasing the drug(https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201300585), transdermal drug delivery (Patent Application no: 1388/DEL/2015) and oral delivery of protein drugs with targeted, controlled and sustained release at a particular pH. (DOI: 10.1039/c5ra07424j DOI: 10.1007/s10965-017-1267-7) Fluorescent gels being developed in our lab intend to be highly efficacious for an improved chemotherapy to specific tissues and cell subpopulations by reducing side effects.(10.1021/acsnano.9b04188)
Wound healingOur invention specifically provides the use of these hydrogels and their nano composites as transparent transdermal wound healing patches for the patient and doctor to be able to visualise the wound and accelerating the healing process, both for normal and diabetic wounds. DOI: 10.1039/C8MH01298A .
Tissue engineeringOur studies are focused on the usage of 3D tissue co-culturing techniques and systems for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. The primary aim of 3D co-culturing is to examine human tissues at laboratory scale as well as in animal models. We have developed and corroborated the as-synthesized novel hydrogel systems as an apt tool for the study of various pathological conditions and an elaborate evaluation of their role and effect in treating diseases associated with brain, intestine, kidney, obesity, diabetes and cancers, which are inclusive of therapeutic screening are underway. Nanogel interfaces are also been employed by our group as imaging tools.
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) allow selective targeting of cytotoxic drugs to cancer cells presenting suitable surface antigens, thereby reducing systemic toxicity. We demonstrated the use of genetically encoded unnatural amino acids with orthogonal chemical reactivity to synthesize homogeneous ADCs with precise control of conjugation site and stoichiometry. (DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211023109) We believe, that the synthesis and characterization of homogeneous ADCs with medicinal chemistry-like control over macromolecular structure should facilitate the optimization of ADCs for a host of therapeutic
We used a cell-based phenotypic screen for inhibitors of biofilm formation in mycobacteria and identified a small molecule TCA1, which has potent bactericidal activity against both drug-susceptible and resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and sterilizes Mtb in vitro combined with rifampicin or isoniazid. TCA1 has bactericidal activity against nonreplicating Mtb in vitro and is efficacious in acute and chronic Mtb infection mouse models both alone and combined with rifampicin or isoniazid. Using genetic and affinity-based methods we identified decaprenyl-phosphoryl-β-D-ribofuranose oxidoreductase DprE1 and MoeW, enzymes involved in cell wall and molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis, respectively, as targets responsible for the activity of TCA1 which may lead to the development of a class of antituberculosis agents. (DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1309171110)
A primary focus of our lab is to design and engineer nano materials with precisely controlled optoelectronic properties. We have developed Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs) from inept biomass, which unlike metal based quantum dots, possess peculiar honeycomb atom arrangement with high quantum yield that enhances its directional and non-directional properties. Additionally they are bestowed with unique rewards of high crystallinity, high photobleaching threshold, water solubility, chemical stability without any surface passivation. These versatile probes combine high quantum efficiency, narrow absorption and wide emission spectral profiles, exceptional biocompatibility affording long term bioimaging and multiplexing, targeted, cavernous anatomical penetration and low scattering making them indispensable in the bioimaging arena. (DOI: 10.1039/C8GC01638K) (Ongoing DST 2018)
The present invention relates to a manufacturing method of substituted urea and carbamate compounds together in one-pot reaction, which are manufactured by making amine, carbon dioxide and alkylene oxide compounds react with each other under an ionic liquid based composite catalyst system with indium wherein substituted urea and carbamate compounds can be manufactured together from amine in high yield, and the ionic liquid based catalyst with indium can be re-used and thus is economical. [US Patent 2016] [DOI: 10.1002/bkcs.11363]; [KR Patent 10-2015-0,055,767].
NANOCATALYSTSThe application of the nanocatalysts is a rapidly growing field for the development of sustainable and green processes. Separation not only avoids the need for catalyst filtration or centrifugation after completion of the reaction, but also provides practical techniques for recovering these catalysts.
WATER REMEDIATION, DYE REMOVAL AND DEGRADATION
We have synthesized different polymers through an effective atom transfer radical polymerization process and resulting polymer was used for the uptake of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Partition coefficient, retention capacity, and metal ion uptake behavior in aqueous solution of PACM at different monomer percent conversions and effect of parameters for optimization of polymerization reaction gives thermally stable PACM. Efficiency of metal ion uptake of different molecular weights of PACM were tested in batches for Ni2+, Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, and Hg2+ ions in single metal solution. DOI: 10.1002/app.38521
We are also scattering information of research work carried out related to various methods for the removal of dyes like Rhodamine-B, Methylene Blue, Crystal Violet, Malachite Green and Safranin-O dye present in textile effluent have been compiled and compared to find out cheap and effective method by calculating their percentage removal.
There is often a design trade-off between effective drug delivery and favorable physicochemical properties however we have engaged in research that address bottlenecks in designing several unique framework of hydrogels for transdermal drug delivery (Patent Application no: 1388/DEL/2015) and oral delivery of protein drugs with targeted, controlled and sustained release at a particular pH. (DOI: 10.1039/c5ra07424j DOI: 10.1007/s10965-017-1267-7) .
Our invention specifically provides the use of biomolecules and their nano composites as transparent transdermal wound healing patches for the patient and doctor to be able to visualize the wound and accelerating the healing process, both for normal and diabetic wounds. DOI: 10.1039/C8MH01298A .
We are working on Hierarchically porous carbon derived from polymers and biomass: effect of interconnected pores on energy applications DOI: 10.1039/C4EE01075B; Advances in conversion of hemicellulosic biomass to furfural and upgrading to biofuels DOI: 10.1039/C2CY20235B; Direct conversion of cellulose and lignocellulosic biomass into chemicals and biofuel with metal chloride catalysts DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2011.12.017. Upgrading furfurals to drop-in biofuels: An overview DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00271.
Catalysis
We are also working on remarkably bent, ethane-linked, diiron (III) μ-oxobisporphyrin: synthesis, structure, conformational switching, and photocatalytic oxidation DOI: 10.1021/ic801423g; and Rational design of Fe catalysts for olefin aziridination through DFT-based mechanistic analysis DOI: 10.1039/C7CY01283G.
We have developed an one pot synthetic route for catalytic NO2 reduction, ring hydrogenation, and N-alkylation from nitroarenes to generate alicyclic amines using Ru/C-NaNO2 DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.09.012; Ruthenium-Na2CO3 catalyzed one-pot synthesis of ring hydrogenated carbamates from aromatic amines and organic carbonates under H2, DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.09.013; One‐Pot Synthesis of Disubstituted Urea from Carbon Dioxide, Propylene Oxide, and Amines Catalyzed by Imidazolium‐Tetraiodoindate 10.1002/bkcs.11363; and Process for preparing disubstituted urea and carbamate compounds from amines, carbon dioxide, and epoxides . [US Patent 2016] .